Sal shows how to find the size and direction of the magnetic force using F=qvB and the right hand rule.Charged Particles in a Magnetic Field. Magnetic Force Conceptual Questions. A Particle's Trajectory in a Magnetic Field. Video animation showing the magnetic field and force on a charge moving out of the page in a magnetic field that is uniform but changing in strength.A second identical charged particle is moving with speed 2v perpendiculuar to the same magnetic field. The time to complete one full circular. A particle (mass = 5.0 g, charge = 40 mC) moves in a region of space where the electric field is uniform and is given by Ex = 2.5 N/C, Ey = Ez = 0. If the...Electric and magnetic forces both affect the trajectory of charged particles Electrostatic Force and Magnetic Force on a Charged Particle. Recall that in a static, unchanging The magnetic field does no work, so the kinetic energy and speed of a charged particle in a magnetic field remain constant.An electron moves in a circular path perpendicular to a constant magnetic field of magnitude 1.00 mT. The angular momentum of the electron But if the directions of the velocity and field are parallel, there is zero force. So you will have to decide for yourself if this should be regarded as true or false!
Forces: Moving Charges in Magnetic Fields | MIT OpenCourseWare
Suppose that charged particles are shot into a uniform magnetic field at the point $A$ in Fig. It is not necessary that all the particles enter at right angles to the field edge. Figure 29-2(b) shows the trajectories of three particles, all with the same momentum but entering the field at different angles.A charged particle experiences a force when moving through a magnetic field. What happens if this field is uniform over the motion of the charged What path does the particle follow? In this section, we discuss the circular motion of the charged particle as well as other motion that results from a......Of The Trajectory That A Moving Charged Particle Follows In A Uniform Magnetic Field? Ampere's Law Involves Integrating The Magnetic Field In A Closed Volume, On A Closed Area, Or Ampere's Law involves integrating the magnetic field In a closed volume, on a closed area, or...A magnetic field is defined by the force that a charged particle experiences moving in this field, after we account for the gravitational and any additional electric forces possible on the charge. The magnitude of this force is proportional to the amount of charge , the speed of the charged particle...

1-What is the shape of the trajectory of a charged particle moving...
• Magnetic fields around moving charged particles • Magnetic fields around current carrying conductors • Magnetic fields around permanent magnets or electromagnets. In HSC Physics, we generally don't care about the source of the magnetic field as the geometry of the field lines in the...Trajectory A is possible when-the magnetic field is in the direction of movement of charged particle, that is into the page. Because in this condition the magnetic force is zero as magnetic field and velocity are parallel to each other.east direction.Just like charges, magnetic poles also produce a field - the magnetic field. And other magnets detect the field at the points they are positioned and then get Assuming no other forces act on the particle the positively charged particle will move in a circular path in the x,z plane. If the magnetic field is...A particle with charge q and mass m moves in a horizontal plane at right angles to a uniform vertical magnetic field B. (a) What are the period... Determine the slope at A. Take E = 29(10 3 ) ksi. The moment of inertia of each segment of the frame is indicated in the figure. Assume D is a pin support.There is a Lorentz force acting on a charged particle in an electromagnetic field. The shape of the trajectory. Remark: The motion of a particle in a uniform electromagnetic field could be compared to the motion of the tire valve of a moving wheel.
Presentation on theme: "Reading Quiz 2. What is the shape of the trajectory that a charged particle follows in a uniform magnetic field? Helix Parabola Circle Ellipse Hyperbola."— Presentation transcript:
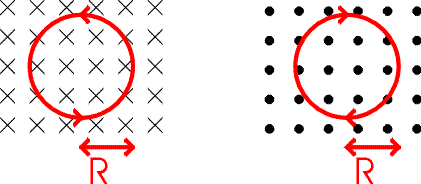
1 Reading Quiz 2. What is the shape of the trajectory that a charged particle follows in a uniform magnetic field? Helix Parabola Circle Ellipse Hyperbola What is the SI unit for the strength of the magnetic field? Gauss Henry Tesla Becquerel Bohr magneton Answer: C
2 Reading Quiz 3. The magnetic field of a level charge is given throughBiot-Savart's law. Faraday's regulation. Gauss's regulation. Ampère's law. Einstein's legislation. 4. The magnetic field of a instantly, current-carrying wire is parallel to the twine. within the wire. perpendicular to the twine. around the cord. 0. Answer: E
3 What is the SI unit for the strength of the magnetic field?Gauss Henry Tesla Becquerel Bohr magneton
4 What is the shape of the trajectory that a charged particle follows in a uniform magnetic field?Helix Parabola Circle Ellipse Hyperbola
5 The magnetic field of a level price is given by way ofBiot-Savart's legislation. Faraday's legislation. Gauss's legislation. Ampère's law. Einstein's law.
6 The magnetic field of a instantly, current-carrying cord isparallel to the wire. within the twine. perpendicular to the cord. round the wire. 0.
7 White board your effects. In specific:Field Around Magnet Use a compass to map the direction of the magnetic field surrounding a magnet. White board your effects. In explicit: how does the energy of the field vary with distance from the twine? how does the field course relate to the poles of the magnet? General Physics 2 Magnetism
8 Activity: Map Field of MagnetsUse iron filings to map the field of a bar magnet horseshoe magnet White board effects draw field lines. how may magnets generate magnetic fields? General Physics 2 Magnetism
9 course of magnetic field, B, is parallel to field line Magnetic Field Lines direction of magnetic field, B, is parallel to field line quantity of lines consistent with house is proportional to power of field field strains point from N to S field traces form closed loops General Physics 2 Magnetism
10 Magnetism No magnetic monopoles! General Physics 2 Magnetism
11 Magnets are similar to Electric DipolesGeneral Physics 2 Magnetism
12 Ferromagnetism Ferromagnetic subject matter Preferentially Random downwardsiron or different materials that can also be made into magnets You can make a magnet from iron by putting it in a robust B field person domains transform aligned with exterior B field Loss of magnetism from: losing heating Curie temperature 1043 Okay for iron Preferentially downwards Random General Physics 2 Magnetism
13 Cross Product – Right Hand RuleGeneral Physics 2 Magnetism
14 Specifying 3 Dimensionsout of page tip of arrow into web page tail of arrow General Physics 2 Magnetism
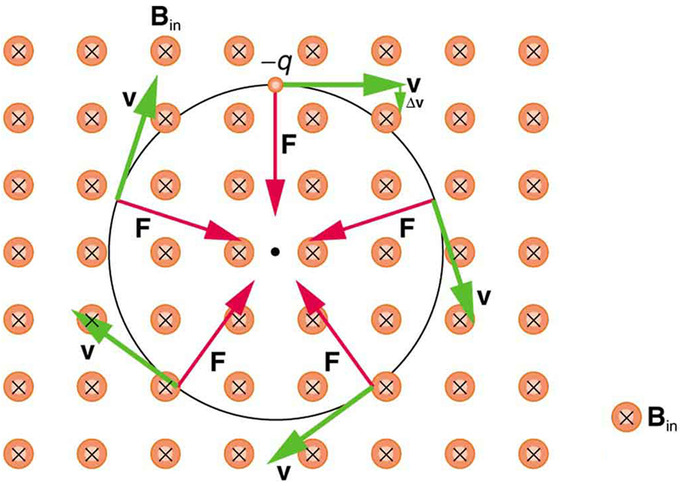
15 Force on a shifting priceRight Hand Rule (#2) qv = arms B = bend hands F = thumb Find the path of the pressure on a detrimental price for each and every diagram shown. General Physics 2 Magnetism
16 General Physics 2 Magnetism
17 Think-Pair-Share Derive an expression for the radius of an e-'s orbit in a uniform B field. Express your resolution in terms of me, v, qe, and B. Turn in your solution! Start of elegance 2 - scholars have already finished worksheets 1 & 2 General Physics 2 Magnetism
18 Earth's Magnetic Fieldmagnetic declination angular distinction between geographic north and magnetic north varies with latitude General Physics 2 Magnetism
19
20
21 Tactics: Right-hand rule for fields
22 The Source of the Magnetic Field: Moving ChargesThe magnetic field of a charged particle q shifting with speed v is given through the Biot-Savart law: where r is the distance from the fee and θ is the attitude between v and r. The Biot-Savart law may also be written in terms of the move product as
23 EXAMPLE 33.1 The magnetic field of a protonQUESTION:
24 EXAMPLE 33.1 The magnetic field of a proton
25 EXAMPLE 33.1 The magnetic field of a proton
26 EXAMPLE 33.1 The magnetic field of a proton
27 The Magnetic Field of a CurrentThe magnetic field of a long, instantly cord carrying recent I, at a distance d from the twine is The magnetic field at the heart of a coil of N turns and radius R, carrying a latest I is
28 EXAMPLE 33.4 The magnetic field power close to a heater wireQUESTION:
29 EXAMPLE 33.4 The magnetic field strength near a heater cord
30 Magnetism: Worksheets 1 and 2 Finish before next classPractice Problems Magnetism: Worksheets 1 and 2 Finish prior to subsequent magnificence General Physics 2 Magnetism
31
32 Tactics: Finding the magnetic field course of a latest loop
33 Magnetic Dipoles The magnetic dipole second of a latest loop enclosing a space A is defined as The SI units of the magnetic dipole second are A m2. The on-axis field of a magnetic dipole is
34 EXAMPLE 33.7 The field of a magnetic dipoleQUESTIONS:
35 EXAMPLE 33.7 The field of a magnetic dipole
36 Tactics: Evaluating line integrals
37 Ampère's regulation Whenever overall current Ithrough passes through a space bounded via a closed curve, the line integral of the magnetic field around the curve is given by means of Ampère's law:
38 The energy of the uniform magnetic field inside of a solenoid iswhere n = N/l is the number of turns per unit length.
39 The Magnetic Force on a Moving FeeThe magnetic power on a rate q because it moves via a magnetic field B with velocity v is where α is the attitude between v and B.
40
41 Magnetic Forces on Current-Carrying WiresConsider a section of wire of period l carrying latest I in the path of the vector l. The wire exists in a consistent magnetic field B. The magnetic force on the wire is the place α is the attitude between the direction of the current and the magnetic field.
42 EXAMPLE 33.13 Magnetic LevitationQUESTION:
43 EXAMPLE 33.13 Magnetic Levitation
44
45 General Principles
46 General Principles
47 General Principles
48 Applications
49 Applications
50 Applications
51 Does the compass needle rotate clockwise (cw), counterclockwise (ccw) or not at all?STT32.1 Answer: C
52 Does the compass needle rotate clockwise (cw), counterclockwise (ccw) or by no means?STT32.1
53 The magnetic field at the position P pointsInto the web page. Up. Down. Out of the page. STT32.2 Answer: D
54 The magnetic field at the place P issuesInto the page. Up. Down. Out of the web page. STT32.2
55 The certain fee is transferring instantly out of the pageThe certain fee is moving instantly out of the web page. What is the route of the magnetic field at the place of the dot? Left Right Down Up STT32.3 Answer: C
56 The positive fee is transferring directly out of the pageThe positive price is moving straight out of the page. What is the route of the magnetic field at the position of the dot? Left Right Down Up STT32.3
57 What is the current direction in this loopWhat is the latest course in this loop? And which side of the loop is the north pole? Current counterclockwise, north pole on bottom Current clockwise; north pole on bottom Current counterclockwise, north pole on top Current clockwise; north pole on most sensible STT32.4 Answer: B
58 What is the current route in this loopWhat is the recent direction in this loop? And which facet of the loop is the north pole? Current counterclockwise, north pole on backside Current clockwise; north pole on bottom Current counterclockwise, north pole on best Current clockwise; north pole on most sensible STT32.4
59 An electron strikes perpendicular to a magnetic fieldAn electron strikes perpendicular to a magnetic field. What is the route of ? Left Into the web page Out of the web page Up Down STT32.5 Answer: B
60 An electron strikes perpendicular to a magnetic fieldAn electron strikes perpendicular to a magnetic field. What is the path of ? Left Into the web page Out of the web page Up Down STT32.5
61 What is the latest route in the loop?STT32.6 Answer: B Out of the web page at the top of the loop, into the web page at the backside. Out of the web page at the bottom of the loop, into the page at the most sensible.
62 What is the latest route in the loop?STT32.6 Out of the page at the best of the loop, into the web page at the backside. Out of the page at the backside of the loop, into the page at the most sensible.
63 Which magnet or magnets produced this prompted magnetic dipole?a or d a or c b or d b or c any of a, b, c or d STT32.7 Answer: B
64 Which magnet or magnets produced this triggered magnetic dipole?a or d a or c b or d b or c any of a, b, c or d STT32.7
Tutorial solutions 2010

ANSWER Correct Part B Which particle if any is negatively ...

Assignment 9 - Assignment 9 1\/18 Assignment 9 Due 11:59pm ...

geometry - What is an "arc of a helix"? - Mathematics ...

In a certain region, electric field E exists along the x ...

Solved: Four Particles Enter A Rectangular Region Of Unifo ...

ANSWER left right ANSWER particle A particle B particle C ...

Circular motion in a magnetic field
PPT - Reading Quiz PowerPoint Presentation, free download ...

ANSWER Correct Part B Which particle if any is negatively ...

Solved: Five Equal-mass Particles (A-E) Enter A Region Of ...

Magnetic Confinement

Circular Motion in a Magnetic Field | Study.com

Solutions to H.C.Verma Part 1 by Jatan Mehta - Issuu

11.4: Motion of a Charged Particle in a Magnetic Field ...

Motion of a Charged Particle in a Magnetic Field ...
PPT - Chapter 32 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ...

PPT - Quiz des cinq constitutions canadiennes PowerPoint ...

A proton enters a uniform magnetic field and follows ...

An electron and a proton moving with the same speed enter ...
A particle of charge +q and a mass m is moving under class ...

0 comments:
Post a Comment